
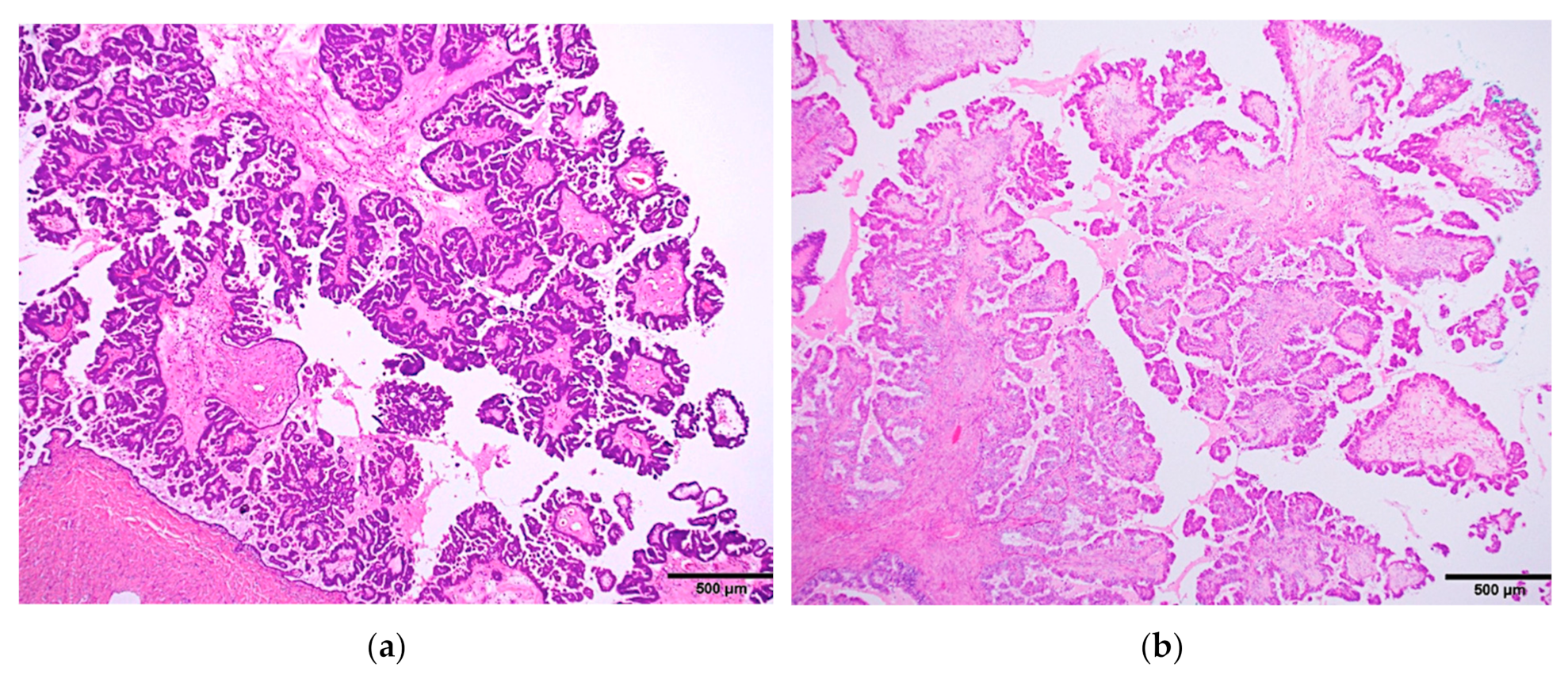
Stage 3: cancer has spread beyond the pelvic region to the abdominal cavity or lymph nodes.Stage 2B: cancer has spread anywhere else in the pelvic region.Stage 2A: cancer has spread to the uterus.Stage 2: cancer has spread beyond the ovaries into the pelvic region.Stage 1C: cancer is in one or both ovaries and the tumor ruptures before or during surgical removal, causing cancer cells to spread.Higher FIGO stages mean the cancer has spread beyond the ovaries. These stages use the International Federation of Obstetrics and Gynecology (FIGO) staging system. There are four stages of serous ovarian cancer, according to the CDC. Taking hormone replacement therapy after menopause can increase your risk of ovarian cancer. For instance, your risk of serous ovarian cancer is higher if you have never given birth or did not give birth until 35 or later. Your risk for serous ovarian cancer can be impacted by past childbirth, pregnancy, and other reproductive health milestones. People with these heritages have a higher incidence of a genetic mutation in the BRCA gene, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). You’re at a greater risk for serous ovarian cancer if you have Northern European or Ashkenazi Jewish heritage.

Studies show that obesity can increase your risk for serous ovarian cancer. Your risk for serous ovarian cancer increases with age, especially after menopause. A family history of any type of ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, or breast cancer increases your risk of developing serous ovarian cancer. Having certain genetic conditions, like Lynch syndrome, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, can also increase your risk of serous ovarian cancer. Mutations in either gene cause a significant increase in your lifetime risk for ovarian cancer. Serous ovarian cancer is linked to an inherited genetic mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene. However, there are several known risk factors that have been shown to increase your chances of ovarian cancer. The exact cause of serous ovarian cancer is still unknown, according to the Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance (OCRA). Causes and risk factors for serous ovarian cancer


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
