

When only air is flowing into the larynx, the inlet to the larynx is open wide, with the free edge of the epiglottis projecting superiorly and anteriorly. They are located below the hyoid bone on the anterolateral surface of the thyroid gland and are involved in movements of the hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage. The lower end of the epiglottis is attached to the deep surface of the thyroid cartilage. The epiglottis is elastic cartilage, shaped like a spoon, that is posterior to the root of the tongue. The function of the cricoid cartilage is to provide attachments for laryngeal muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing of the airway to produce sound.

The lower border marks the inferior limits of the larynx and pharynx. muscle Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle Middle scalene Middle thyroid. The cricoid cartilage is shaped like a signet ring, with the broad part of the ring facing posteriorly. cricothyroid ligament larynx vocal cords thyroid cartilage Phonetics - The. The superior laryngeal vessels and the internal laryngeal nerve pierce the membrane en route to providing vascular supply and sensory information, respectively, to the mucosa superior to the vocal folds.
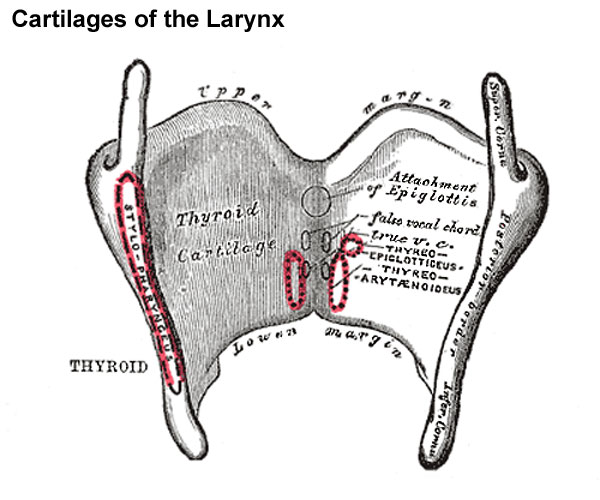
The thyroid cartilage typically is larger in males than in females because the male sex hormones stimulate its growth during puberty. The thyroid cartilage forms a median elevation, called the laryngeal prominence (“Adam's apple”), and lies inferior to the hyoid bone. Severe spasm can cause pain during swallowing( Odynophagia).

Motor incoordination of the cricopharyngeus can cause difficulty swallowing. Uncoordinated contraction, and/or spasm and/or impaired relaxation of this muscle are currently considered the main factors in development of a Zenker's diverticulum. The inferior fibers are horizontal and continuous with the circular fibers of the esophagus the rest ascend, increasing in obliquity, and overlap the Constrictor medius.Īs soon as the bolus of food is received in the pharynx, the elevator muscles relax, the pharynx descends, and the constrictores contract upon the bolus, and convey it downward into the esophagus. The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is one of three pharyngeal constrictor muscles whose main function is to facilitate the process of deglutition. On the thyroid cartilage it arises from the oblique line on the side of the lamina, from the surface behind this nearly as far as the posterior border and from the inferior cornu.įrom these origins the fibers spread backward and medialward to be inserted with the muscle of the opposite side into the fibrous raphé in the posterior median line of the pharynx.From the cricoid cartilage it arises in the interval between the Cricothyreoideus in front, and the articular facet for the inferior cornu of the thyroid cartilage behind.The components arising from the cricoid and thyroid cartilages are also known as cricopharyngeus and thyropharyngeus respectively.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
